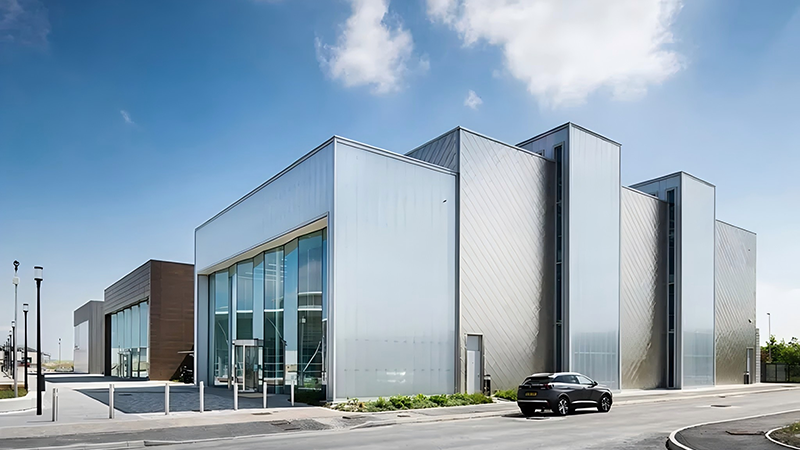
Definition of Polycarbonate Facades
Polycarbonate facades refer to an exterior facade or cladding system that utilizes polycarbonate sheets as the primary material. Polycarbonate is a type of high-performance plastic known for its exceptional strength, lightweight nature, and transparency, making it an innovative choice for modern architectural designs.
Unlike traditional materials such as glass or wood, polycarbonate is lightweight and durable, providing architects and designers with the flexibility to create innovative designs without compromising on safety or structural integrity. Its excellent thermal insulation properties and UV resistance further enhance its appeal, ensuring that buildings remain comfortable and energy-efficient year-round.
This guide aims to serve as a comprehensive resource for understanding polycarbonate facades, covering everything from their types and properties to installation and maintenance practices. Whether you are an architect, builder, or property owner, this guide will equip you with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions regarding the use of polycarbonate facades in your projects.
By exploring the many benefits and considerations associated with this versatile material, we hope to inspire you to incorporate polycarbonate facades into your architectural vision, contributing to a more sustainable and aesthetically pleasing built environment.
Types of Polycarbonate Facade Sheets
Polycarbonate sheets are available in various forms, each designed to meet specific needs and applications. Below are the most common types of polycarbonate sheets:
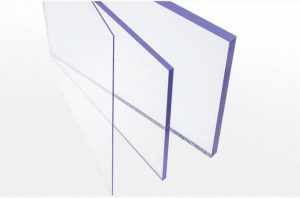
- Solid Polycarbonate Sheets
These sheets are completely solid and provide high impact resistance while maintaining clarity similar to glass.
Applications: Ideal for applications requiring transparency and strength, such as skylights, security glazing, and protective barriers.
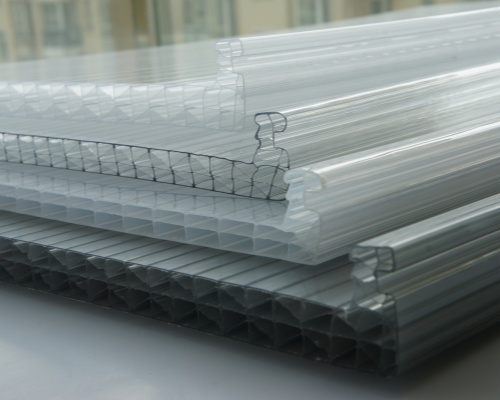
- Twin-Wall Polycarbonate Sheets
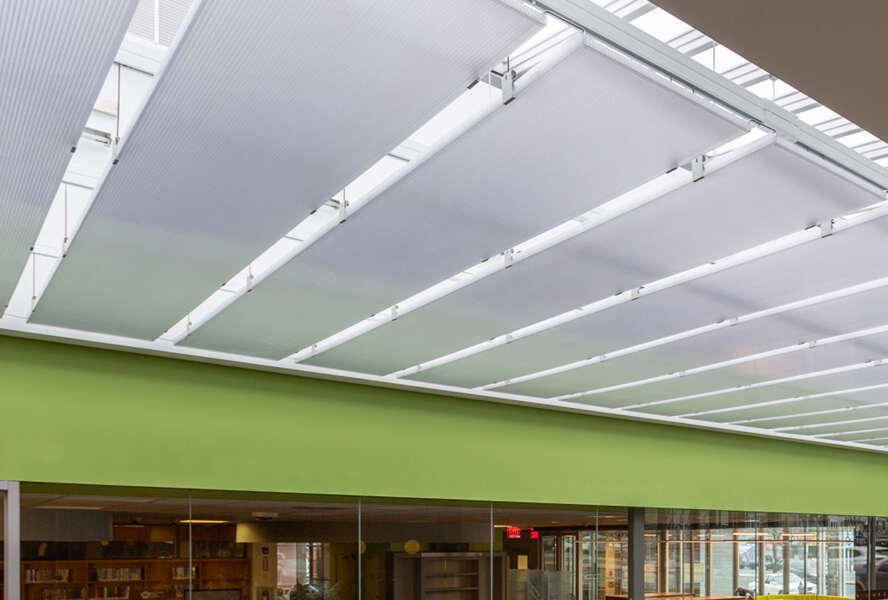
Also known as twin-wall polycarbonate, these sheets consist of two layers with an air gap in between. They are lightweight yet provide good insulation.
Applications: Commonly used in greenhouses, lighting applications, and semi-transparent walls where thermal performance is needed.

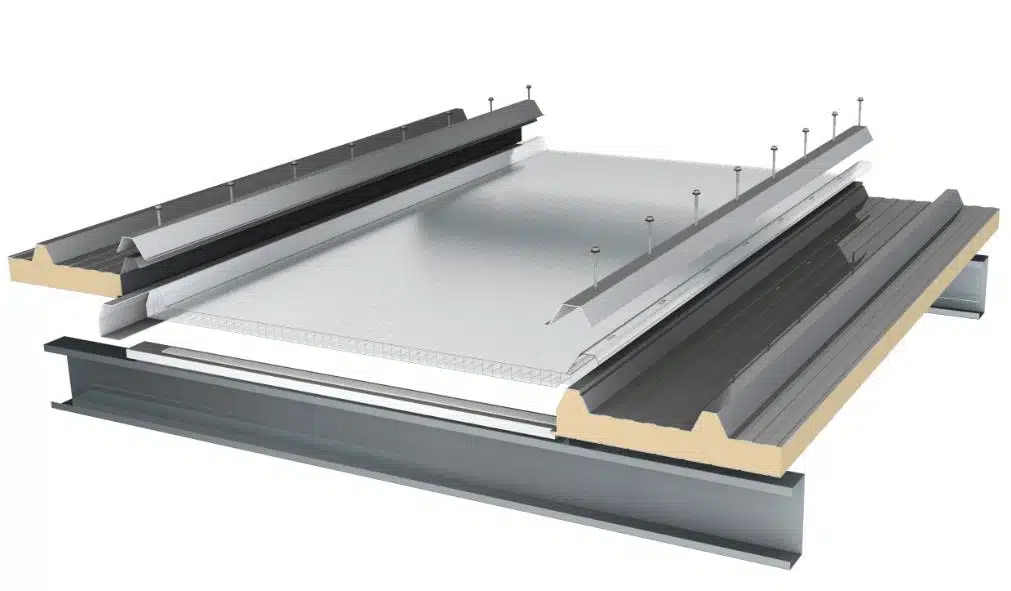
- Multi-Wall Polycarbonate Sheets
Featuring multiple layers and air chambers, this type offers excellent thermal insulation and rigidity while remaining lightweight.
Applications: Often utilized in large panels for roofing, walls, and canopies, where energy efficiency and structural stability are essential.

- Corrugated Polycarbonate Sheets
These sheets have a wavy or corrugated structure, which enhances their strength and rigidity. They are often lightweight and easy to install.
Applications: Commonly used for roofing, greenhouse structures, and as cladding materials in industrial and agricultural settings.
- Specialty Polycarbonate Sheets
These types of polycarbonate sheets with unique features, such as:
Frosted Polycarbonate: Offers a translucent finish for privacy while diffusing light.
Tinted Polycarbonate: Available in various colors to reduce glare and solar heat gain.
UV-Filtered Polycarbonate: Provides enhanced protection against UV radiation, suitable for outdoor applications.
Applications: These sheets are used in situations requiring specific aesthetic or functional properties, such as signage, decorative panels, and protective coverings.

Properties of Polycarbonate Facades
Polycarbonate is a high-performance thermoplastic material known for its excellent combination of physical, mechanical, and thermal properties. Below are the key properties that make polycarbonate a popular choice for a wide range of applications, particularly in construction and architectural design:
1. Strength and Durability
Polycarbonate is renowned for its exceptional strength, making it resistant to impacts and mechanical stress. It is often used in situations where safety and durability are paramount.
2. Impact Resistance
Polycarbonate can withstand high impact forces without cracking or breaking, making it an ideal material for safety applications, such as glazing and protective barriers.
3. Thermal Insulation
Polycarbonate sheets, particularly multi-wall and twin-wall varieties, provide excellent thermal insulation. The air pockets between layers help reduce heat transfer, contributing to energy efficiency in buildings.
4. Temperature Resistance
Polycarbonate can maintain its integrity and performance in a wide range of temperatures, typically from -40°C to 120°C (-40°F to 248°F), making it suitable for diverse environmental conditions.
5. Optical Properties
Polycarbonate allows for high levels of light transmission (up to 90%) while offering various levels of transparency. This makes it a suitable alternative to glass in many applications.
6. UV Resistance
Many polycarbonate sheets come with UV coating, protecting from harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays while minimizing material degradation over time.
7. Lightweight Characteristics
Polycarbonate is considerably lighter than traditional materials like glass and metal, making it easier to handle, transport, and install without the need for heavy structural support.
8. Flexibility and Formability
The material can be easily molded and shaped, allowing for creative designs and applications. It can be fabricated into various forms and thicknesses to meet specific project requirements.
9. Weather Resistance
Polycarbonate exhibits excellent resistance to weathering, including resistance to rain, snow, and extreme sunlight. It does not warp or degrade easily when exposed to the elements.
10. Fire Resistance
While polycarbonate is combustible, it has a high ignition point and can be treated for improved fire resistance, making it suitable for building applications where fire safety is a concern.
11. Chemical Resistance
Polycarbonate generally shows good resistance to a variety of chemicals, including oils and alkalis, but may be sensitive to certain solvents. It is essential to ensure compatibility with specific chemicals used in its environment.
12. Ease of Maintenance
Polycarbonate facades and applications require minimal maintenance compared to other materials, as they are resistant to fading and corrosion. Regular cleaning with mild soap and water is usually sufficient.
Advantages of Polycarbonate Facades
Polycarbonate facades offer numerous benefits that make them an attractive choice for architects, builders, and property owners. Here are some of the key advantages of using polycarbonate facades in construction:
1. Energy Efficiency
- Thermal Insulation: Polycarbonate sheets, particularly those designed with multi-wall structures, provide excellent thermal insulation, reducing heat transfer and improving energy efficiency in buildings. This helps to lower heating and cooling costs.
- Natural Light Utilization: The high light transmission properties of polycarbonate allow natural light to enter interior spaces, reducing the need for artificial lighting during the day.
2. Impact Resistance
- High Durability: Polycarbonate is highly resistant to impacts, making it ideal for areas prone to vandalism or extreme weather conditions. It can withstand heavy blows without cracking or breaking, providing safety and longevity.
3. Lightweight and Easy to Install
- Reduced Structural Load: Polycarbonate is significantly lighter than traditional materials like glass, which reduces the overall weight on building structures and can simplify design requirements.
- Ease of Installation: The lightweight characteristics of polycarbonate make it easier to handle and install, resulting in faster construction times and lower labor costs.
4. Versatile Design Options
- Aesthetic Flexibility: Polycarbonate sheets are available in various colors, textures, and finishes, allowing for creative design possibilities. Architects can create modern, visually appealing facades that enhance the overall aesthetics of a building.
- Customizability: Polycarbonate can be easily cut, molded, and shaped to fit unique architectural designs, enabling the realization of complex geometric forms and innovative facades.
5. Weather and UV Resistance
- Durability Against the Elements: Polycarbonate exhibits excellent resistance to weathering, including rain, snow, and UV radiation. This ensures that it maintains its appearance and structural integrity over time.
- UV Protection: Many polycarbonate sheets come with UV-filtering properties, protecting interior spaces and preventing material degradation due to sun exposure.
6. Low Maintenance Requirements
- Minimal Upkeep: Polycarbonate facades require less maintenance compared to traditional materials. They are resistant to corrosion and fading, and cleaning them typically involves simple washing with soap and water.
7. Cost-Effectiveness
- Affordable Material: Polycarbonate is often more cost-effective than materials such as glass or metal, both in terms of material costs and installation expenses. Its long lifespan further contributes to its overall value.
8. Safety Features
- Shatter Resistance: Unlike glass, polycarbonate does not shatter upon impact, which enhances safety, especially in public spaces and areas where breakage could result in injury.
- Fire Retardant Options: While polycarbonate is a combustible material, fire-retardant versions are available, providing added safety in construction projects where fire codes must be met.
Disadvantages and Limitations of Polycarbonate Facades
While polycarbonate facades offer numerous advantages, there are some disadvantages and limitations to consider when selecting this material for architectural applications. Understanding these drawbacks is essential for making informed decisions. Here are some key disadvantages and limitations of polycarbonate facades:
1. Scratch Sensitivity
- Surface Vulnerability: Polycarbonate is more prone to scratching compared to traditional materials like glass. Scratches can affect the aesthetics and clarity of the facade, potentially diminishing its visual appeal over time.
2. Temperature Sensitivity
- Thermal Expansion and Contraction: Polycarbonate can expand and contract significantly with temperature changes. Proper installation techniques must be followed to accommodate this movement, or it may lead to warping or buckling.
3. Potential for Yellowing
- UV Exposure Effects: Over time, exposure to UV radiation can lead to yellowing of polycarbonate sheets, especially in lower-quality products. While many sheets contain UV stabilizers to mitigate this effect, it is essential to choose high-quality options for long-term applications.
4. Limited Fire Resistance
- Combustibility: Although polycarbonate has certain fire-resistant properties, it is still a combustible material. In applications where fire safety is a major concern, special fire-retardant grades may be necessary, which can increase costs.
5. Compatibility with Chemicals
- Chemical Sensitivity: Polycarbonate may be sensitive to certain solvents, adhesives, and chemicals. Care should be taken during construction and maintenance to avoid using incompatible substances that may lead to degradation.
6. Noise Transmission
- Acoustic Performance: Polycarbonate facades may not provide the same level of sound insulation as some traditional materials. In applications where noise reduction is critical, additional soundproofing measures may be necessary.
7. Initial Costs and Budgeting
- Cost Compared to Traditional Materials: While often more affordable than glass, polycarbonate can still be more expensive than some traditional materials, which may affect budget considerations. Additionally, if opting for specialized polycarbonate sheets with enhanced properties, costs can rise significantly.
8. Limited Load-Bearing Capacity
- Structural Support Constraints: While polycarbonate is strong, it may not have the same load-bearing capabilities as materials like metal or glass. Careful consideration of structural requirements is essential when designing with polycarbonate.